- August 18, 2021
- admin
- 0 Comments
- Uncategorized
Industry 4.0
Knowledge and timely adoption of upcoming trends is the key to success in this ever changing and competitive environment. Technology is transforming business models and as challenges for the manufacturing industry are growing, manufacturers need to transform.
Indian industry cannot shy away from adopting such technological transformations such as Industry 4.0 standards and practices, which is the current trend of automation and principles of data exchange in manufacturing technologies
Industry 4.0 is a significant step closer to reality, paving the way to profitable plants with high availability. It takes transformation – digitalization solutions to realize innovation, performance, thereby realizing their own digital enterprise.
What is Industry 4.0?
Industrialization started with steam and the first machines that mechanized some of the work that our ancestors did. Subsequently, with the evolution of electricity, the assembly lines and the birth of mass production came into being. The third era of industry came in with the advent of computers and the beginning of automation when robots and machines began replacing workforce on those assembly lines.
The basic principle of Industry 4.0 is that by connecting machines, work pieces and systems, businesses shall create intelligent networks along the entire value chain that can control each other autonomously.
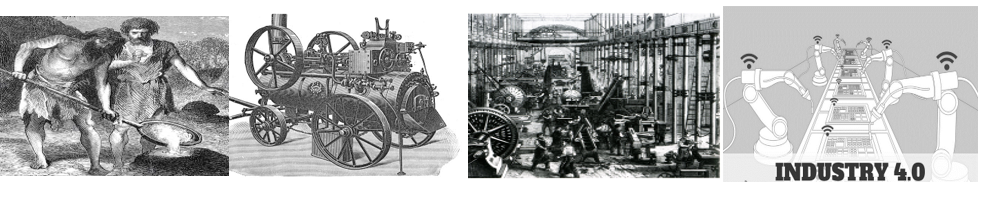
Industry 4.0 introduces what has been called the “smart factory,” in which cyber-physical systems monitor the physical processes of the factory and make decentralized decisions. Industry 4.0 runs on a framework of Internet of things (IoT), cloud and cognitive computing to create smart manufacturing.
The underlying design principles behind Industry 4.0 are:
- Interoperability — machines, devices, sensors and people that connect and communicate with one another.
- Information transparency — the systems create a virtual copy of the physical world through sensor data to contextualize information.
- Technical assistance — both the ability of the systems to support humans in making decisions and solving problems and the ability to assist humans with tasks that are too difficult or unsafe for humans.
- Decentralized decision-making — the ability of cyber-physical systems to make simple decisions on their own and become as autonomous as possible.
What are the Challenges in Industry 4.0:
- Data security issues are greatly increased by integrating new systems and more access to those systems. Additionally, proprietary production knowledge becomes an IT security problem as well.
- A high degree of reliability and stability are needed for successful cyber-physical communication that can be difficult to achieve and maintain.
- Maintaining the integrity of the production process with less human oversight could become a barrier.
- Loss of high-paying human jobs is always a concern when new automations are introduced.
- And avoiding technical problems that could cause expensive production outages is always a concern.
- Additionally, there is a systemic lack of experience and manpower to create and implement these systems — not to mention a general reluctance from stakeholders and investors to invest heavily in new technologies.
But the benefits of an Industry 4.0 model could outweigh the concerns for many production facilities. In very dangerous working environments, the health and safety of human workers could be improved dramatically. Supply chains could be more readily controlled, when there is data at every level of the manufacturing and delivery process. Computer control could produce much more reliable and consistent productivity and output. And the results for many businesses could be increased revenues, market share, and profits.
Impact of Industry 4.0 on SMEs
Despite the challenges, most agree that Industry 4.0’s impact on the SMEs will be significant. It has the potential to disrupt both processes and products. There could be a 360-degree change in the way the sector is operating now. The hurdles faced by these Small and Medium Scale Enterprises(SMEs) in areas of monitoring and decision making about the manufacturing process could see a massive make over with the industry 4.0.
With the Industry 4.0, machines shall predict failures and trigger maintenance processes autonomously or self-organized logistics which would react to unexpected changes in production.
In addition to condition monitoring and fault diagnosis, components and systems will be able to gain self-awareness and self-predictive capability, which will provide management with more insight on the status of the factory. Furthermore, peer-to-peer comparison and fusion of health information from various components will provide a precise health prediction in component and system levels and force factory management to trigger required maintenance at the best possible time to reach just-in-time maintenance and gain near-zero downtime

Leave a Comment